
Also, with multiple copies of data, it’s easy for the two systems to get out of sync and for analysts to work with outdated information.ģ. The replication can be done at the source systems, the ETL layer, the DW layer (via mirrored backup), or the DW storage system. In addition, the BI team must establish and maintain a utility to replicate the data to the sandbox, which may take considerable expertise to create and maintain. Executives may question why they need a separate machine to handle tasks they thought the DW was going to handle. Organizations must purchase, install, and maintain a separate database platform-which may or may not run the same database and server hardware as the DW. Of course, the downside to this is cost and duplication of data.
#DEFINITION OF ANALYTICAL SANDVOX FREE#
DW performance improves significantly without a costly upgrade, and analysts get free reign of a box designed exclusively for their use. This approach offloads complex, ad hoc queries issued by a handful of people to a separate machine, leaving the production DW to support standardized report delivery, among other things. Many companies have begun to physically separate the production DW from ad hoc analytical activity by purchasing specialized DW appliances. One way to avoid performance problems and systems management complexities is to replicate the DW to a separate platform designed exclusively for analysts.
#DEFINITION OF ANALYTICAL SANDVOX UPGRADE#
Inevitably, the BI team may need to upgrade the DW platform at considerable expense to support the additional workload.Ģ. An organization that has dozens or hundreds of analysts, each of whom wants to create large data sets and run complex queries, may bog down performance even with workload management rules in place. Database administrators must create and maintain partitions and access rights and tune workload management utilities to ensure adequate performance for both general DW users and business analysts. However, a DW-centric sandbox can be difficult to manage from a systems perspective. It’s also easier for the BI team to convert analyses into production applications since the analytic output is already housed in the DW. These DW-centric sandboxes preserve a single instance of enterprise data (i.e., they don’t replicate DW data), make it easier for database and DW administrators to observe what analysts are doing, and help analysts become more comfortable working in a corporate data environment. The traditional analytic sandbox carves out a partition within the data warehouse database, upwards of 100GB in size, in which business analysts can create their own data sets by combining DW data with data they upload from their desktops or import from external sources. Nonetheless, many BI teams are employing analytic sandboxes with reasonable success.ġ. Ultimately, organizations that establish sandboxes must establish policies and procedures for managing information in a consistent manner and provide sufficient education about proper ways to produce and distribution information. Analysts can still export data sets to their desktop machines, email results to colleagues, and create unauthorized production applications. Unfortunately, analytic sandboxes can’t enforce information policies. If analysts want to convert what they’ve created into a scheduled report or application, they need to turn it over to the BI team to “productionize” it. 90 days), reinforcing the notion that they are designed for ad hoc analyses, not application development. Ideally, sandboxes come with an expiration date (e.g.
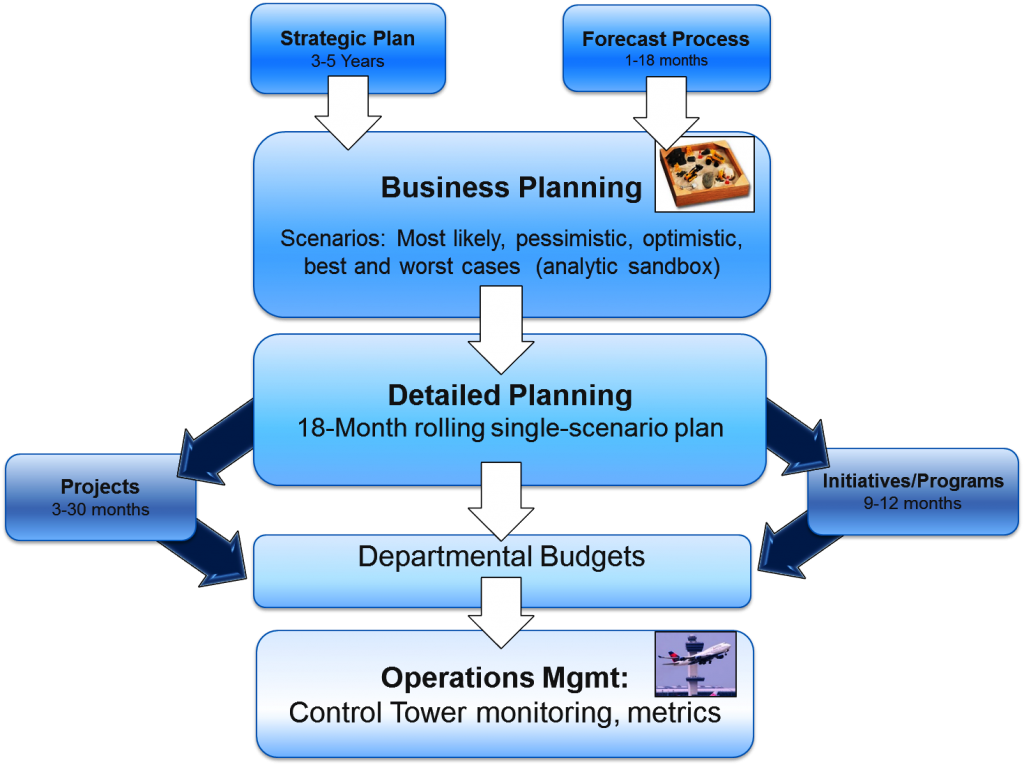
Many BI teams already provide sandboxes of some sort, but few recognize that there are three tiers of sandboxes that can be deployed individually or in concert to meet the unique needs of every organizationĪnalytic sandboxes adhere to the maxim, “If you can’t beat them, join them.” They provide a “safe haven” for business analysts to explore enterprise data, combine it with local and external data, and then massage and package the resulting data sets without jeopardizing an organization’s proverbial “single version of truth” or adversely affecting performance for general DW users.īy definition, analytic sandboxes are designed for exploratory analysis, not production reporting or generalized distribution. Three Tiers of Analytic Sandboxes: New Techniques to Empower Business AnalystsĪnalytic sandboxes are proving to be a key tactic in liberating business analysts to explore data while preventing the proliferation of spreadmarts and renegade data marts.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
